Portugal is divided into 14 Regional Wine areas : Vinho Verde, Trás-os-Montes, Porto and Douro, Távora-Varosa, Bairrada, Dão, Beira Interior, Lisboa, Tejo, Península de Setúbal, Alentejo, Algarve, Açores and Madeira.
Portuguese wine is then categorized using the ‘DOC’ (Denominação de Origem Controlada) system meaning Controlled Denomination of Origin. Portugal has 31 DOCs/DOPs. At the moment, both the traditional terminology of DOC and the new pan-European “DOP” are used. DOP (Denominação de Origem Protegida) means Protected Denomination of Origin. The “DOC/DOP” system is similar to the Denominación de Origen “DO” system of Spain, the Appellation d’origine contrôlée “AOC” system of France and the Denominazione di origine controllata “DOC” of Italy.
In the Douro there are separate DOCs for unfortified wine and for Port, although geographically they both lie within the same boundaries.

DOURO VALLEY
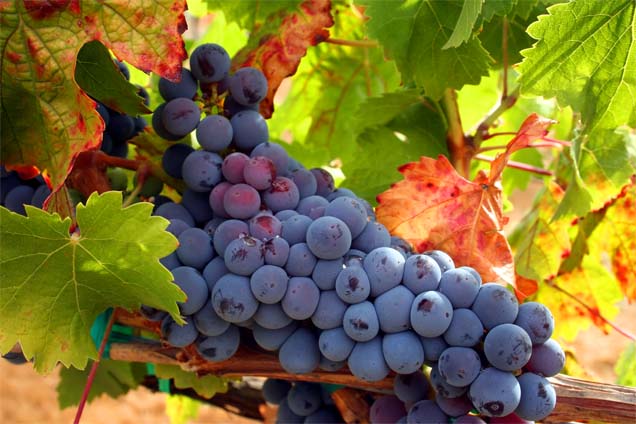
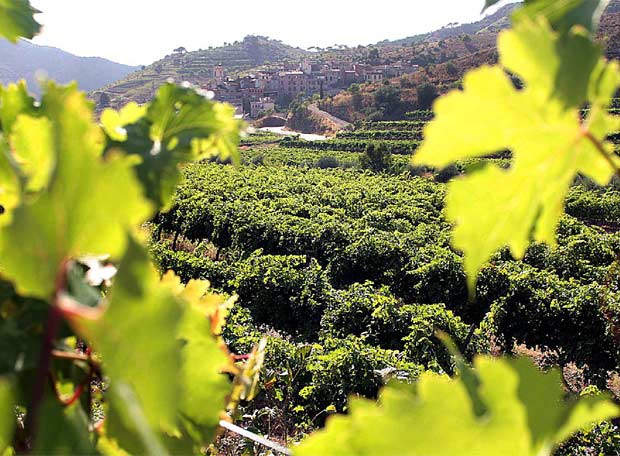
The Douro Valley, Portugal, is considered one the most spectacular wine regions of the world with its terraced vineyards on sloping hills that meet the meandering River Douro below as it cuts through the mountains. The characteristic terraces of vines in the Douro Valley were introduced by the Romans in the third century A.D and the Douro “vinhateiro” wine-growing area of the Douro Valley is now a designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The soil in which the Douro Valley vines are planted is made up of schist, a slate-like metamorphic rock. Rich in nutrients, it also has useful water retention properties.
Long famous as the source of Port Wine, the authentic port wine is made at ‘quintas’ (estates) along a narrow river gorge that winds 100 miles through the mountain ranges and was once shipped downriver to the city of Porto in sailboats called ‘barcos rabelos’. But, the Douro Valley not only produces fortified wine. Around the same amount of unfortified wine is produced and is renowned for its fine and rich red and white wine.
The Douro wine region of Portugal is divided into three sub-regions: Baixo Corgo, Cima Corgo and Douro Superior from west to east respectively. The further east, the drier the climate becomes and the deeper the wines. The Cima Corgo, which includes the towns of Pinhão, São João da Pesqueira and Tua, is the heart of fine port production and where also many of today’s fine unfortified wines are produced.
- The Baixo Corgo lies at the western end, closest to the Marão mountains, where the rainfall and vineyard yields are highest. This area mainly produces the lighter more early maturing styles of Port intended to be drunk relatively young.
- The Cima Corgo area is the location of many of the Douro’s finest vineyards and produces more concentrated and long lasting wines.
- The Douro Superior is the easternmost area and is the driest of all making it the source of many of the finest Vintage Ports.
Main white Douro Valley grapes:
- Viosinho, Malvasia Fina, Gouveio, Rabigato, Côdega, Donzelinho Branco, Esgana Cão and Folgazão
Main red Douro Valley grapes:
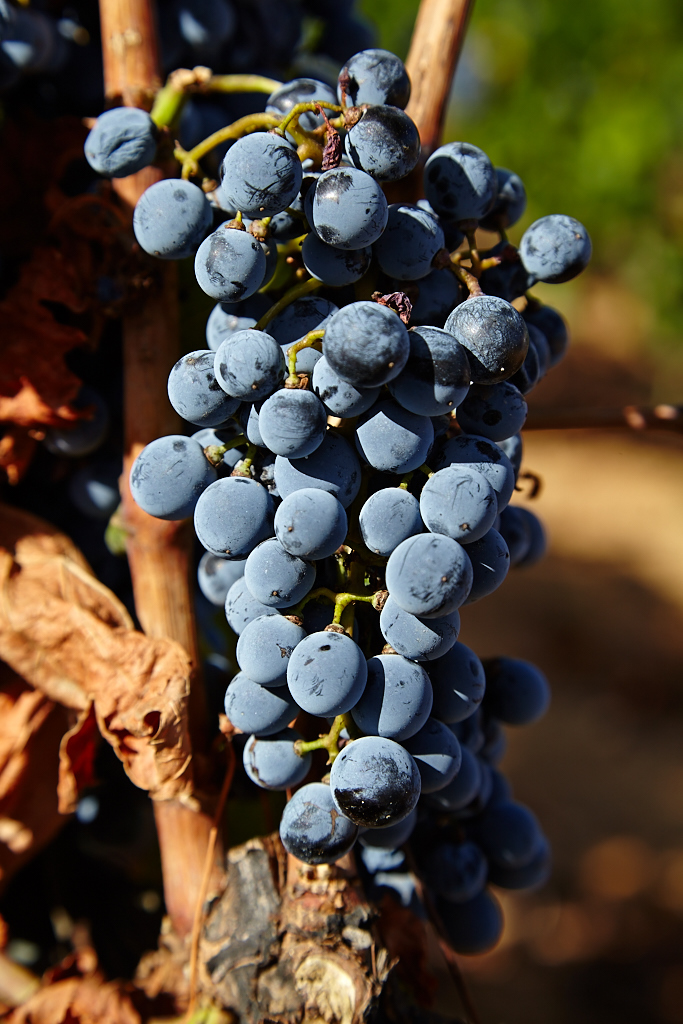
- Touriga Nacional, Tinta Roriz (Aragonez), Touriga Franca, Tinta Barroca, Tinto Cão, Sousão, Bastardo, Mourisco Tinto, Castelão, Rufete, Tinta Amarela (Trincadeira) and Tinta Francisca
Just some of the World class Quintas that you could be visiting in the Douro Valley:
Quinta do Crasto – Sitting in a privileged location in the Douro Demarcated Region, this Quinta is famous for its sophisticated wines as well as for the dramatic views. This single vineyard property dates as far back as the early seventeenth century, long before the Douro became the world’s first demarcated wine region in 1756
Quinta do Seixo – Sandeman’s flagship, and a most exclusive port winery, of the most important Port wine producer. This Winery is beautifully maintained and picturesquely located just down the river from Pinhao, with gorgeous views of Pinhao.
Quinta do Panascal – This majestic quinta, whose reputation goes back to the 18th century, is located on the banks of the river Távora. It is the most important estate of the prestigious Port Wine Company “Fonseca Guimaraens”.
Quinta de la Rosa – Quinta de la Rosa is unusual in the way that they do everything in the Douro. Most port houses make their port in the Douro but store and bottle it in Vila Nova da Gaia, in Porto. Here, you will be able to see both wine and port making processes side by side.

PORT WINE
Port Wine is a wine that was developed in Portugal by the British. It is a by product of their battles with France through the 17th and 18th centuries. The English finally decided to boycott French wine in the late 17th century and began sourcing their red wine from Portugal. They started to add a drop of Brandy to the still wine so that it would arrive in England after the long trip on a rocky boat without spoiling. This addition of the brandy not only gave the wine the strength to survive the journey but it also made the wine considerably sweeter when it was added early enough to stop fermentation.
Today, Port wine ferments for only 2 to 3 days, has brandy added, and then is aged in wooden barrels. How long it ages determines the taste and how sweet the wine is.
The base for Port is made and fortified in wineries in the Douro Valley, then transported to the Port lodges of Vila Nova de Gaia, opposite Porto, at the mouth of the river, for ageing. Here, the ageing and blending of most of the world’s supply of Port wine takes place beneath a sea of red roofs emblazoned with some of the most famous names in wine-making. Rabelo boats were traditionally used to carry the wine down the river from Douro to the lodges in Oporto.
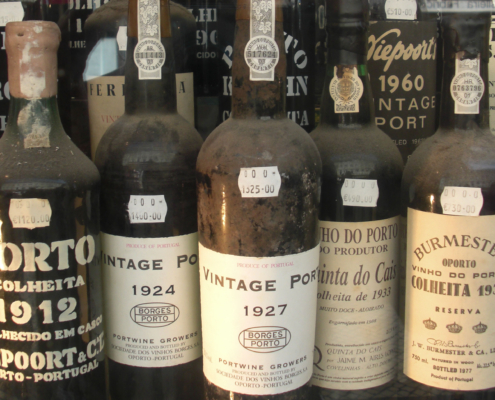
There are generally five different types of port wine – white, ruby, tawny, late bottle vintage (LBV), and vintage. White is aged early and is young and robust. Ruby is aged for 3 years with a strong grape and pepper taste. Tawny is aged in smaller wooden barrels and varies from 10 to 40 years (the label will specify how many 10, 20, 30, 40) with a lighter color and a more mellow taste. Late Bottle Vintage is aged 4 to 6 years while vintage is from a single harvest and is bottled after only two years in barrel, keeping it rich and red, then 10 to 30 years in the bottle. All port wines are medium sweet but they do range from a drier, less sweet to very sweet.
Although around thirty grape varieties can be used to make Port Wine, the five red grape types now generally considered to produce the finest port wine are: Tinta Roriz, Touriga Franca, Touriga Nacional, Tinta Barroca and Tinto Cão.
Just some of the fantastic Port Wine Lodges that you could be visiting in the Porto:
Taylor’s Port Wine Lodge – One of the oldest of the founding Port houses was established over three centuries ago in 1692. For many, Taylor’s is the archetypal Port house and its wines the quintessential Ports. It is dedicated entirely to the production of Port wine and in particular to its finest styles. The history of the firm is in many ways the history of the Port trade itself.
Graham’s Port Wine Lodge – For almost two hundred years W & J Graham’s has been an independent family business renowned for producing some of the finest Port wines. Wine Spectator Magazine voted Dow’s 2011 as the best port Wine in 2014. Dow’s Lodge in Porto is not open for visitors, but Graham’s is their sister company and you can buy the awarded Port here.
Sandeman Port Wine Lodge – Founded in 1790 the Sandeman Lodge is housed in a former 16th century convent with a small museum. The Sandeman Porto Cellars are a landmark spot and the building boasts one of the best views of Porto.

Join us on a Private Tour of Portugal (or a combined tour with Spain) like our Luxury Tour of Portugal – Wine and Culture to experience the beautiful Wine Regions of Portugal in Alentejo and the Douro Valley, among others, to enjoy winery visits and tastings as well as a relaxing picnic in a vineyard and a cruise along the Douro River.






















 Located partly within the Basque country, Rioja DOCa Wine Region of Spain is perhaps best known for red wines and the Tempranillo grape. The Rioja Spanish Wine DO Ca region’s red wines cover many different styles from young wines through to more sophisticated wines which are capable of many years of cellaring – proving the versatility of Tempranillo. Some producers also offer white wines, including some fine barrel-fermented and oak-aged styles and rosés. The best known of the Spanish wine DO regions, Rioja Spanish Wine DOCa carefully preserves its wine styles but interestingly there are some modern trends which are starting to show through.
Located partly within the Basque country, Rioja DOCa Wine Region of Spain is perhaps best known for red wines and the Tempranillo grape. The Rioja Spanish Wine DO Ca region’s red wines cover many different styles from young wines through to more sophisticated wines which are capable of many years of cellaring – proving the versatility of Tempranillo. Some producers also offer white wines, including some fine barrel-fermented and oak-aged styles and rosés. The best known of the Spanish wine DO regions, Rioja Spanish Wine DOCa carefully preserves its wine styles but interestingly there are some modern trends which are starting to show through.